The length of the Earth’s day and its orientation are caused by humans Climate Change A new study has revealed that the Sun is constantly changing the Earth’s rotation.
While initially these changes will be imperceptible to us, researchers warn that they could set off serious knock-on effects, including forcing us to introduce negative leap seconds, disrupting space travel and even altering the Earth’s inner core.
Start of the day Earth The Earth’s rotation period is approximately 86,400 seconds. However, the time it takes for the Earth to complete one rotation varies by a few milliseconds each year due to various factors, including tectonic movements and crustal movements. Changes in the rotation of the inner core And the pull of gravity Moon.
But human-induced climate change is another factor that could change the length of our day, and scientists are only just beginning to realise how much this will affect the Earth’s rotation in the coming years.
Over the past few decades, the Earth’s poles, especially Greenland and Antarcticateeth, global warmingThis causes sea levels to rise. Most of this extra water accumulates near the equator, causing the Earth’s center to bulge slightly. As a result, the Earth’s rotation slows down because weight is distributed away from the center of the Earth. This is similar to when a figure skater moves their arms away from their body as they spin to slow down.
A new study published July 15 in the journal Neurology & Neurology, PNASThe researchers artificial intelligence A program that combines real-world data with the laws of physics to predict how a planet’s rotation will change over time.
Related: Everything you need to know about Earth
Result is, Similar studies The predictions, released in March, suggested that Earth’s days would get longer in the future, but the new projections offer a much more accurate prediction of how the days will get longer over time.
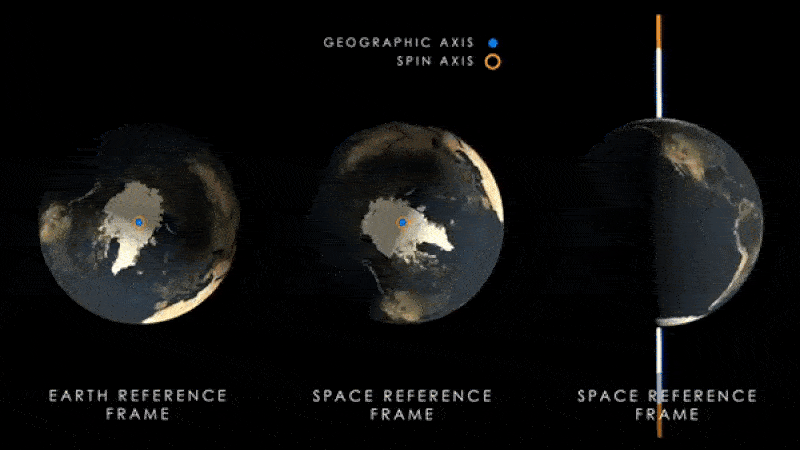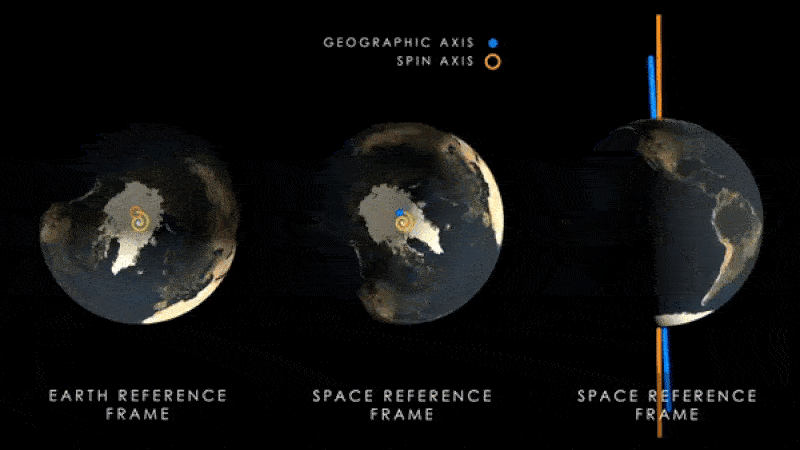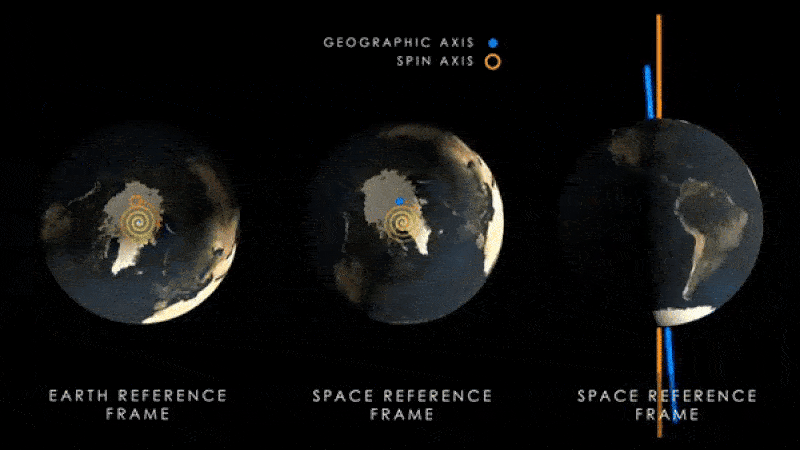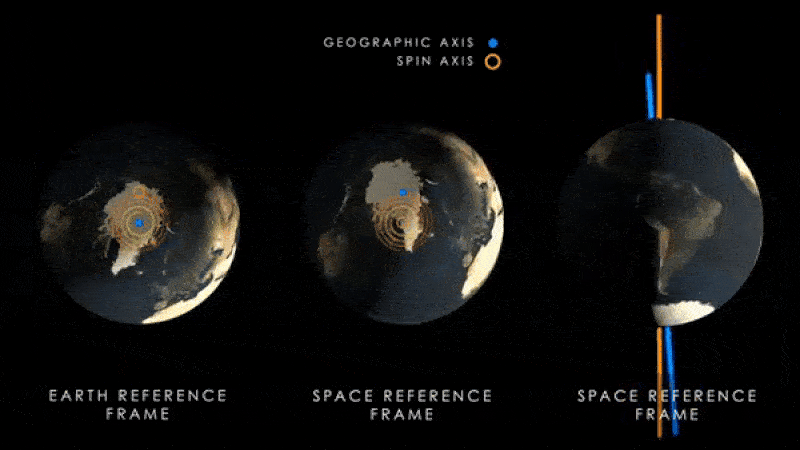
The same research team behind the new paper also published another study in the journal Neurology on July 12. Nature Chemistryshowed that an increase in water near the equator is shifting the Earth’s axis of rotation, which causes the magnetic poles to swing away from the axis each year.
Scientists have previously shown that this effect This has likely happened at least for the past 30 years.However, new research suggests that the axis may move further from its current position than previous studies had predicted.
“We humans have a much bigger impact on the planet than we realize.” Benedict Soya“The study is a step forward for the science community,” said Gregory B. Schneider, a geodesist at ETH Zurich in Switzerland and co-author of the two new studies. statement“And of course, this places a huge responsibility on us for the future of the planet.”
Rotation is slow
Earth Days The length is constantly changingAbout 1 billion years ago, the Earth Only 19 hours to complete one rotationand then slow down to the 24-hour period we are experiencing today.
Changes also occur on shorter time scales. For example, in 2020, the Earth It’s spinning faster than any other time records have been kept. 1960. In 2021, the planet’s rotation will be It started to slow down again we The shortest day in history June 2022.
But in general, Earth’s rotation has been slowing down for millennia, mainly due to a phenomenon called lunar tidal friction, where the moon’s gravitational effect on the oceans pulls water away from the poles. Currently, this effect lengthens the day by about 2.3 milliseconds every century.
Climate change is currently lengthening the length of daylight by about 1.3 milliseconds per century, according to a new study, but based on current global temperature models, researchers predict that this could increase to 2.6 milliseconds per century by the end of the 21st century, when climate change would have the greatest impact on Earth’s rotation.
Potential impact

One of the most likely effects of longer days is the need to introduce negative leap seconds, which would result in the occasional loss of one second on some future dates as the days get longer. How leap years work.
A March study suggested this may need to start as soon as 2029, mainly to accommodate how much longer daylight hours have already become over the past few thousand years.
In the past, scientists have suggested that this introduction Time management for computers and smartphonesBut not everyone is convinced this will be a big problem.
The researchers of the new study said future changes could also have implications for space travel.
“Even if the Earth’s rotation is changing only slowly, this effect needs to be taken into account when navigating space – for example, when landing a space probe on another planet,” Soja said, adding that it is therefore important to closely monitor such changes.
The team also warned that shifts in Earth’s axis could alter the rotation of the planet’s inner core, making the days get longer even faster — though this potential interaction is still poorly understood.