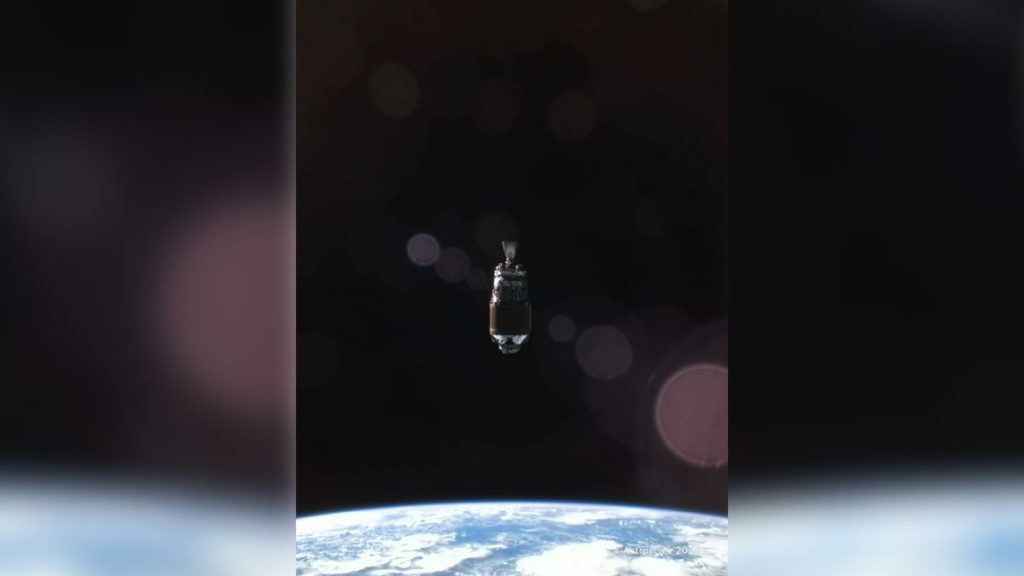
Astroscale Japan has released even more startling images of space debris in Earth’s orbit.
The Tokyo-based company launched its Active Debris Removal Spacecraft (ADRAS-J) aboard a Rocket Lab Electron rocket. February 18, 2024ADRAS-J is designed to test safe approach and investigation methods. Space debris This will be done in orbit through a maneuver called Rendezvous Proximity Operation (RPO).
To test the spacecraft’s capabilities, Astroscale sent ADRAS-J to photograph the upper stage of a decommissioned Japanese H-2A rocket. rocket The company released a statement on July 9th, showing new images of the wreckage floating against a blue and white sky. Earth The sunlight is reflected and it’s dazzling.
ADRAS-J took the photos sometime in June 2024 from a distance of just 165 feet (50 meters) from the bus-sized H-2A upper stage rocket, which is about 36 feet (11 meters) long and weighs 3 tons.
In addition to photographing space debris, ADRAS-J also demonstrated a collision avoidance system, including autonomous operation, using the RPO equipped with a failed upper stage rocket. In fact, while approaching the rocket body, the Astroscale spacecraft detected an attitude (orientation) anomaly and stopped autonomously.
ADRAS-J was then able to move away from the debris, demonstrating that this capability allows the spacecraft to “remain safe while approaching and conducting observations of uncooperative objects,” Astroscale wrote. statement.
Such close-quarters operations require delicate maneuvering, as much of the space debris, such as the H-2A’s upper stage, was not designed with such missions in mind.
Astroscale has high hopes for ADRAS-J. Commercial Debris Removal Demonstration After the completion of CRD2, the company acquired the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) plans to remove and deorbit large chunks of so-called “uncooperative” space junk that were not designed for such a deorbit mission.
“This next step is significant in addressing the space debris problem and laying the foundation for a sustainable environment for future generations,” said Eddie Kato, president of Astroscale Japan. Previous statement.
Phase 2 of the CRD2 mission is scheduled to begin after 2026.