More than 200,000 people in the United States Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, this is the most common form of lupus and is commonly referred to as lupus.
fact
- Lupus is a complex autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the body, producing antibodies that attack the skin, joints and kidneys. brain Or other organs.
- In the study, researchers measured the amount of a certain type of white blood cell called T cells in blood samples taken from lupus patients compared with a control group. Subjects with lupus had higher levels of a specific type of T cell that is associated with producing antibodies that attack the body.
- The researchers traced the chain of events in the immune system and identified insufficient receptor activity in T cells. Aryl Hydrocarbonsis considered as a potential underlying cause of the disease.
- Researchers are now investigating whether new therapies could activate that receptor and change the behavior of T cells, ultimately treating autoimmune diseases through a chain of events in the immune system.
- The study was done in a lab and used blood samples from a small number of lupus patients. Future studies are needed to determine whether the findings can be applied more broadly to patients with other autoimmune diseases.
“This won’t immediately cure lupus, but it will help us understand specific ways to inhibit the abnormal immune response,” Rao said. “We are optimistic that this will lead to new therapies to suppress these autoimmune diseases.”
The study was funded by grants from the medical companies Merck Sharp & Dohme & Co. and Janssen Research and Development, Inc. Co-authors of the study included employees of the biopharmaceutical companies AstraZeneca and Janssen at the time the study was conducted.
Rao said he has submitted a patent application for the drug based on the results of his and his collaborators’ work. Choi Jae Hyuk“These findings suggest that the FDA has a role in preventing and treating rheumatoid arthritis in children and young adults with rheumatoid arthritis,” said lead author of the Nature study. Calvin LawGraduate student at Northwestern University.
What other experts say
While it’s still too early to find a cure, the findings are “a promising avenue to consider and think about in terms of providing a more sophisticated approach to treating lupus,” the researchers said. Anka AskanaseProfessor of Medicine, Director of the Lupus Center and Director of Rheumatology Clinical Trials at Columbia University.
What causes lupus?
There are four main types of lupus: SLE, neonatal and pediatric lupus erythematosus, discoid lupus erythematosus, and drug-induced lupus.
woman, People of Color People with a family history of autoimmune diseases are at higher risk of developing them, for reasons that are not clearly understood.
According to experts, the cause of lupus is unknown, but “Genetic, hormonal, immunological and environmental factors According to one review, “all of these contribute to the development of SLE.”
“Lupus is not an immediately fatal disease like cancer, but it does take a lot from people in terms of their daily lives and life expectancy,” Askanadze says.
What are the symptoms associated with lupus?
Experts say systemic lupus erythematosus can affect many organs and has a wide range of symptoms. People with SLE typically experience fever, fatigue and weight loss.
Pulmonary symptoms of lupus include shortness of breath, cough, and difficulty breathing, while gastrointestinal symptoms include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Cardiovascular symptoms include coronary artery disease, pericarditis, and myocarditis. Some patients also suffer from anemia, leukopenia, and thrombocytopenia. Renal function may also be affected by lupus, 50 percent of patients Nephritis develops.
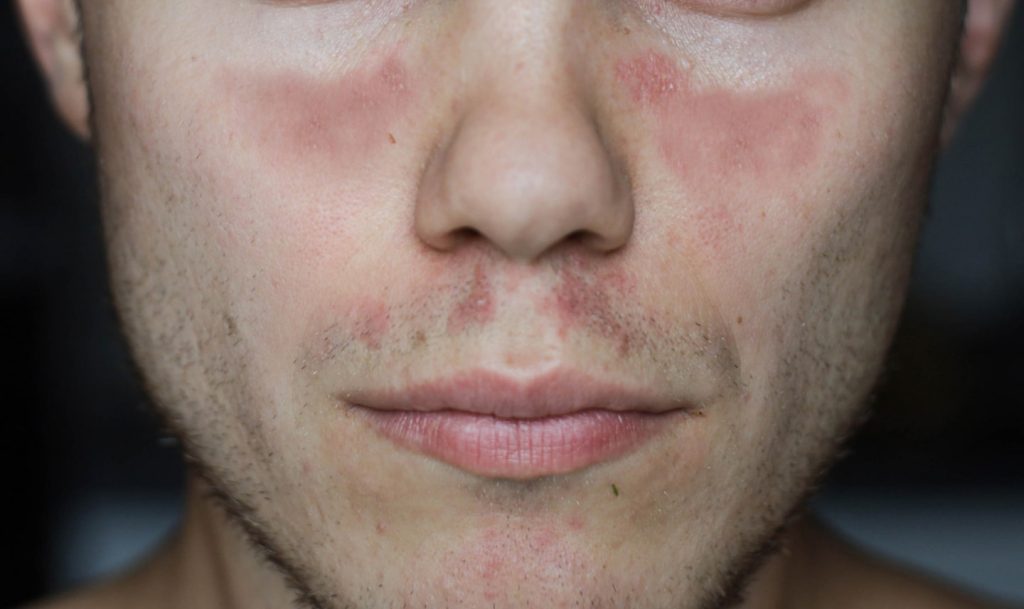
When lupus affects the joints, patients complain of pain, stiffness, and inflammation. They are often diagnosed with arthritis, joint pain, and muscle pain. Patients with skin symptoms often develop a red “butterfly” rash on their nose and cheeks after exposure to sunlight. Other patients: Alopeciasores in the mouth and nose.
depressionWhen lupus affects the central nervous system, symptoms such as anxiety and cognitive impairment appear.
Is there a cure for lupus? How is it treated?
There is no cure for lupus, but treatments are “rapidly evolving.” Karen Costenbader“This is a rare disease that has been linked to a number of side effects,” he said in an email.
“In the past, healthcare professionals have treated the condition with steroids, which can cause serious side effects. However, several new, more targeted immunosuppressants are now available and more are being developed.” Lupus Foundation of America Medical and Scientific Advisory Board.
Several Pharmaceuticals Treatment includes: Hydroxychloroquine and other antimalarial drugs. Many patients take a combination of drugs. These drugs have side effects, some of which are serious.
“Most of the treatments for lupus are still broadly classified as immunosuppressants,” Choi said. “If we can find the molecular root cause of lupus, we may be able to develop safer and more effective treatments.”
Experts say lupus is difficult to diagnose and treat.
“If you have 300 patients in the same room, they’re all going to have different clinical symptoms,” he said. Jill P. Bayondirector of the Rheumatology and Lupus Center at NYU Langone Health, was not involved in the study.
It’s difficult to think of a “one size fits all” treatment, she says, and the findings from this study could perhaps “point us towards precision medicine, where we can segment patients, exactly as Deepak Rao has done so beautifully, and evaluate the treatments that we should give to patients who fit this paradigm.”
“It’s a great paper. It’s incredibly well done,” Buyon said. “Is it the root cause? I don’t know if it’s the root cause. It could be the root cause.”
Are there any new treatments for lupus?
“There are newer biologics, such as belimumab, which targets B-lymphocyte stimulatory factor, and anifrolumab, which blocks proteins called interferons that signal and stimulate lymphocytes,” Kostenbader said.
There are several other drugs in clinical trials that may have potential to treat lupus, she says. “Work with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T lymphocytes has raised hopes that very effective suppression of B-cell responses may pave the way for treatment. The Nature study suggests a different but related strategy, altering the ability of T cells to stimulate abnormal B-cell responses,” she says.
Askanadze said “great progress” and possible treatments have been made thanks to researchers and “the incredible gifts from people who take part in observational studies and clinical trials, and from volunteers.”
What is the impact on other autoimmune diseases?
Several other autoimmune diseases, including Sjogren’s disease and rheumatoid arthritis, have an excess of the T cells found in lupus patients, and the researchers’ proposed treatment “has the potential to be effective in many of these diseases,” Rao said in an email.