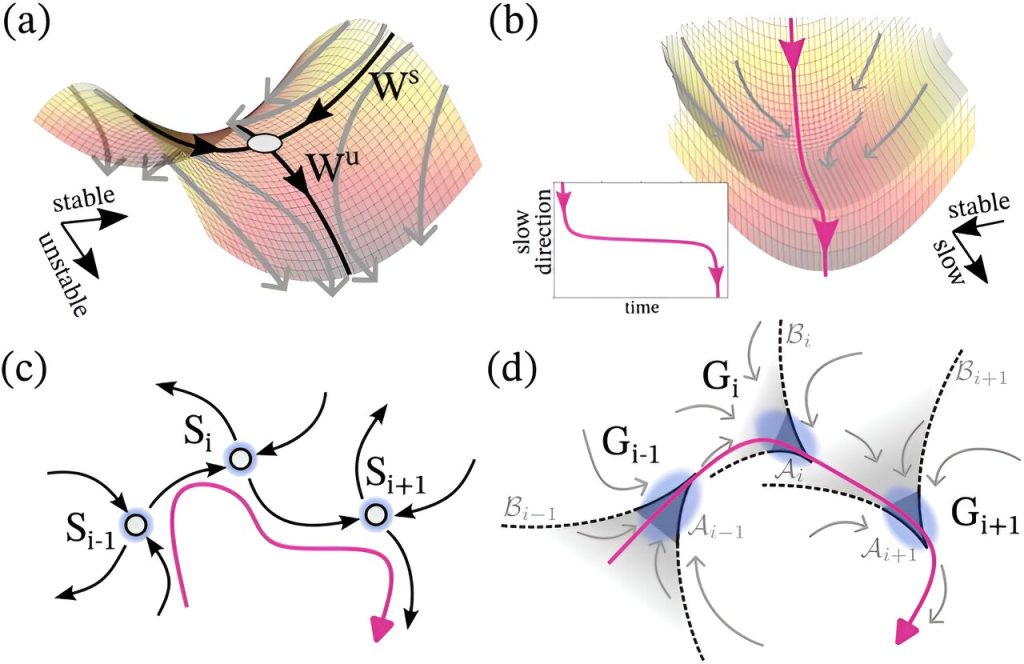
Schematic of phase space objects. (a) Quasipotential landscape of the saddle fixed point. Grey dots: localization of unstable fixed points. (b) Quasipotential landscape of the ghost state. Note the absence of fixed points. Inset: Time course of a trajectory with a slow transition through the ghost. (c) Schematic of the scaffolding of the saddle (𝑆𝑖), i.e., heteroclinic channels, and (d) ghosts (𝐺𝑖), i.e., ghost channel.𝑖 Denote the ghost-attracting set of 𝐺𝑖and 𝐵𝑖 (a)-(d) The black, grey, and magenta arrows represent example (unstable) manifolds, flow directions, and trajectories, respectively. Credit: Physics Review Letter (2024). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.133.047202
Scientists around the world use modeling methods to understand complex natural systems such as the climate system or neural and biochemical networks. A team of researchers has developed a new mathematical framework that, for the first time, explains the mechanisms behind long-term transient behavior in complex systems.
They introduce ghost channels and ghost cycles as new objects to explain how natural systems can be stable for long periods of time, yet rapidly switch to another state.
This new approach challenges traditional concepts based on stable or unstable equilibrium and may help us better understand how temporally stable neuronal dynamics control sensory information processing or predict transformation cascades that lead to biodiversity loss.
The research was conducted by a collaboration between the Max Planck Institute for Behavioral Neurobiology, the University of Leicester and King’s College London. Published In the journal Physics Review Letter.
When you ask for directions in a new city, your working memory temporarily holds chunks of information, such as turns and landmarks to follow in a particular order. But once you reach your destination, you forget the details. To perform this task, neural networks in the brain have the contradictory ability to temporarily stabilize neural activity to remember the information, while at the same time quickly switching to a different state in the sequence.
Similar dynamics are observed in ecology: in competing microbial populations, one species often dominates for long periods of time, Stable equilibrium Suddenly, for no apparent reason, another species begins to dominate, leading to the decline of the previous species. Such transitions can also lead to extinction and biodiversity loss.
To predict if and when such a diversion event will occur, the observed dynamics prior to the diversion are often analyzed. The difficulty with such predictions is that in order to correctly interpret the statistics of the recorded data, prior knowledge is required as to whether the conditions are indeed stable or whether they come from a long transient state.
However, economically important ecosystems, e.g. Coral ReefThere is a need to determine whether reefs that appear to be healthy ecosystems are actually at risk of slipping into a degraded, algae-dominated state.
Challenging conventional dynamics models
Traditionally, dynamical states of complex systems have been described as attractors or equilibria — abstract mathematical objects that can be observed over infinitely long time periods and to which the system is expected to return after small perturbations — but these states do not capture how temporary stability or rapid transitions are achieved.
To introduce both features, dynamic saddle sequences have been explored in the past: they resemble a saddle shape and stabilize the dynamics along one dimension (along the seat), but are inherently unstable and can fall along the orthogonal dimension.
Thus, when an unstable dimension of one saddle is connected to a stable dimension of another saddle, a channel of saddles, called a heteroclinic channel, emerges, allowing the dynamics of the system to switch states in a sequential manner.
The study, led by scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology and Behavior (MPINB) in Bonn, in collaboration with researchers from the University of Leicester and King’s College London, shows that heteroclinic channels cannot fully capture the dynamics observed in real-world noisy systems: their ability to generate temporally stable states along the saddle is quickly lost when the system encounters small perturbations.
In contrast, they identified a special type of instability called ghost channels and ghost cycles, Complex Systems It can exhibit robust temporarily stable behavior, followed by a rapid transition to another temporarily stable state with very different characteristics.
Ghost structures are features that emerge in critical states where a system is balanced on the border of two or more qualitatively distinct regimes. Such configurations allow the system to exploit qualitatively different regimes, thereby effectively balancing opposing features.
Dr Akhilesh Nandan from MPINB explains: “By changing the framework in which dynamics are controlled by stable states, or attractors, to one in which the dynamics are determined by formally unstable structures such as ghost-based scaffolding, we are now able to obtain potential explanations for what has been observed experimentally across a wide range of systems. Critical to defining this framework was the mathematical characterisation of these abstract ghost objects.”
Understanding ecosystem degradation and climate change
In their paper, the scientists demonstrate that their ghost-based scaffolding is able to better capture the characteristics of long transients in noisy systems compared to traditional models. Rather than relying on precise knowledge or the existence of (unstable) fixed points, the new framework centers on slow directional flows organized by ghost channels and ghost sets in ghost cycles.
An intriguing implication of this work is that ghost structures appear to highlight many different processes in biology and biological processes. Natural Systems If you know what to look for.
“We have identified ghost channels in a model relevant to cell fate decisions during development, but also in a model of tipping cascades in the climate system, which will be used to investigate how tipping of, for example, the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) affects the dynamics of other climate subsystems,” says Dr. Daniel Koch.
These new findings therefore open many doors for future research, from a theoretical understanding of how neural networks code smells and tastes, to more accurate predictions of ecosystem and climate change.
“But what excites us most are the possibilities this powerful theoretical framework brings to biology and artificial intelligence research,” says Dr. Aneta Koceska, head of the Cellular Computation and Learning group at MPINB in Bonn. “We have already started to investigate how the ghost scaffold can help natural and artificial neuronal networks learn, and how we can use it to overcome the current catastrophic forgetting obstacle.”
Thus, the framework may not only provide a potential umbrella tool for studying long transients, but also identify limitations of current mathematical frameworks and where further extensions are needed to address long-standing open questions on the dynamics of metastable transients across biological, natural and artificial systems.
For more information:
D. Koch et al. “Ghost Channels and Ghost Cycles Induce Long-Term Transients in Dynamical Systems” Physics Review Letter (2024). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.133.047202
Provided by
Max Planck Society
Quote: Balancing instability and robustness: a new mathematical framework for the dynamics of natural systems (July 26, 2024) Retrieved July 28, 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-07-instability-robustness-mathematical-framework-dynamics.html
This document is subject to copyright. It may not be reproduced without written permission, except for fair dealing for the purposes of personal study or research. The content is provided for informational purposes only.